10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Plastic Tanks for Your Needs
When it comes to storage solutions, plastic tanks often emerge as a versatile and reliable option for various applications. Whether you're in the agricultural sector, a manufacturing unit, or simply managing personal projects, choosing the right plastic tanks can significantly impact efficiency and safety. With so many different types and sizes available on the market, it can be challenging to pinpoint exactly which tank best suits your needs.
This article aims to provide essential tips for selecting the ideal plastic tanks, taking into account factors such as material strength, tank size, and intended use. Understanding the specific requirements of your project or operation is crucial, as it can influence everything from storage capacity to environmental considerations. As we delve into the essential criteria for selecting plastic tanks, you'll gain insights that can help streamline your decision-making process, ensuring you invest in a solution that delivers optimum performance and longevity.
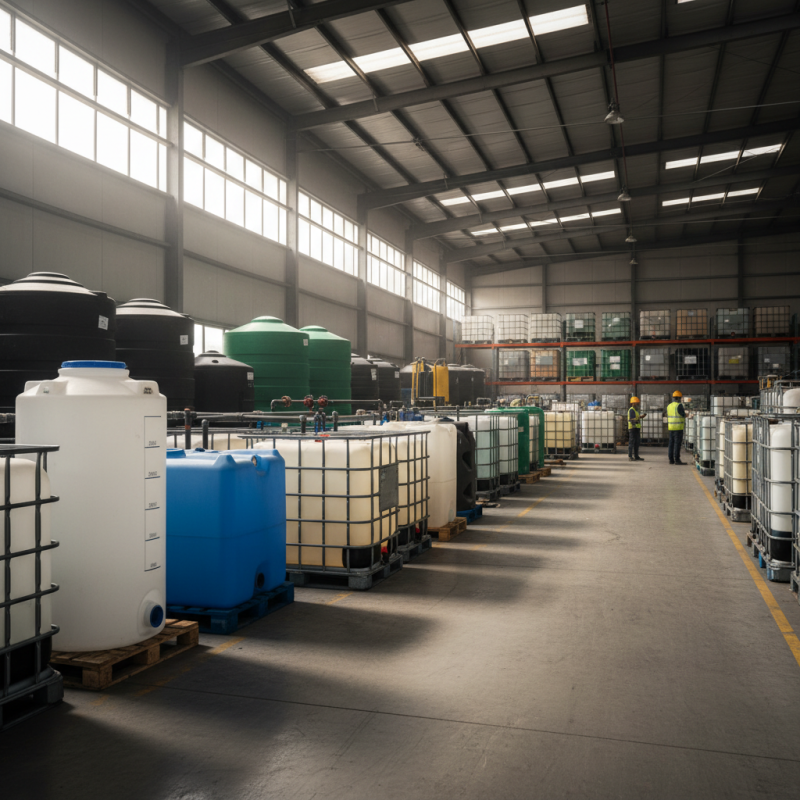

Understanding the Different Types of Plastic Tanks Available in the Market
When it comes to selecting plastic tanks, understanding the various types available is crucial to meet your specific requirements. The most common types of plastic tanks include polyethylene, polypropylene, and PVC tanks. Polyethylene tanks are widely favored for their excellent chemical resistance and durability, making them ideal for storing liquids such as water, chemicals, and fertilizers. According to the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), polyethylene tanks can withstand a wide range of temperatures, typically from -40°F to 120°F, allowing for versatile applications in various climates.
On the other hand, polypropylene tanks are recognized for their higher temperature resistance and strength, which are particularly beneficial in industrial applications. These tanks can endure higher pressures and temperatures, often reaching up to 200°F. Furthermore, PVC tanks are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for storing acidic or alkaline solutions. A recent industry report by Transparency Market Research highlights that the global plastic tank market is projected to grow significantly, driven by increased demand in sectors such as agriculture and water treatment. Thus, knowing the distinct characteristics of each tank type is essential in making an informed decision for your storage needs.
Key Factors to Consider: Size and Capacity Requirements for Your Application
When selecting plastic tanks for various applications, understanding size and capacity requirements is crucial. According to the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), the volume capacity of plastic tanks can greatly influence not only the storage efficiency but also the operational effectiveness of the processes they serve. For instance, industries such as agriculture, wastewater treatment, and food processing often have specific volume requirements that dictate the type and size of plastic tanks to be utilized. It is recommended to have a clear assessment of both current and projected needs, ensuring that the chosen tank can accommodate fluctuations in usage, thereby preventing overflows or shortages.
Additionally, it's important to consider the dimensions and physical aspects of the tank. A report from the Plastic Water Tank Market by Research and Markets highlights that tanks come in various shapes and sizes to suit specific installation spaces, from vertical cylinders to horizontal designs. Sampling spaces prior to selection allows for an accurate fit and helps avoid costly remodeling. Furthermore, establishing a safety margin on top of the desired capacity can be beneficial, as it ensures that the tank will not be under excessive pressure and remains within acceptable weight limits, which is especially pertinent when determining the tank's placement and mounting requirements. Overall, understanding size and capacity is foundational to making informed decisions when choosing plastic tanks for specific applications.
10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Plastic Tanks for Your Needs
| Factor |
Considerations |
Examples |
| Size |
Determine the physical dimensions needed for your application. |
50 Gallon, 100 Gallon, 250 Gallon |
| Capacity |
Calculate the total volume required. |
500 Liters, 1000 Liters |
| Material |
Select materials based on chemical compatibility. |
Polyethylene, Polypropylene |
| Orientation |
Choose vertical or horizontal tanks based on space. |
Vertical tanks are space-saving. |
| Temperature Resistance |
Assess if tanks can withstand temperature variations. |
Use for hot or cold liquids as needed. |
| UV Protection |
Consider UV-resistant tanks for outdoor use. |
Opaque tanks prevent algae growth. |
| Maintenance |
Evaluate ease of cleaning and upkeep. |
Smooth surfaces ease cleaning. |
| Budget |
Determine how much you can afford. |
Plastic tanks range from $100 to $500. |
| Regulatory Compliance |
Ensure tanks meet local regulations. |
Food grade, chemical compliance standards. |
Material Selection: Comparing Polyethylene, Polypropylene, and Other Plastics
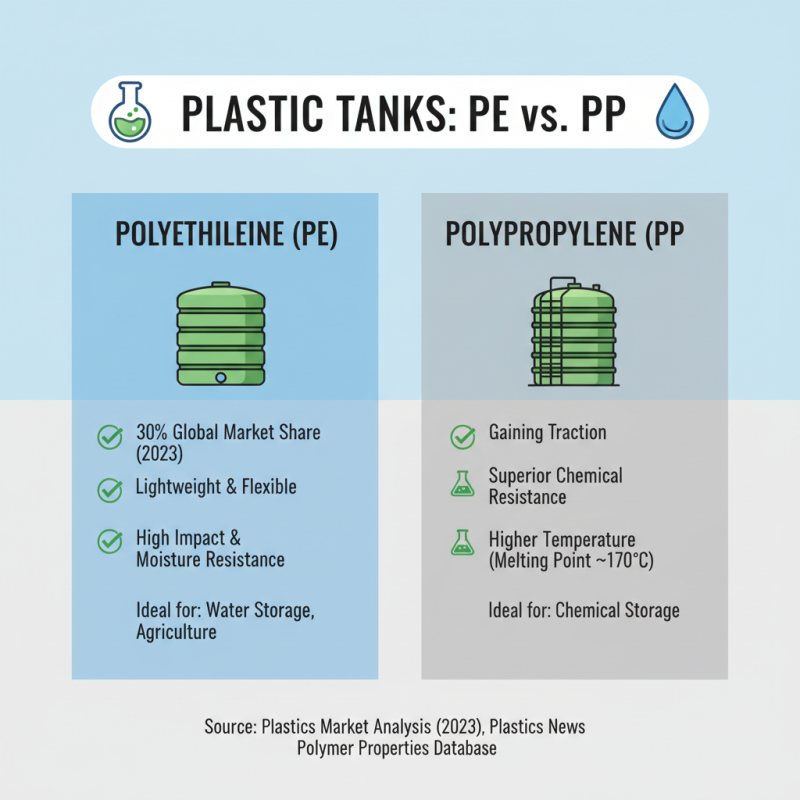
When selecting the right plastic tanks for various applications, understanding the properties of different materials is crucial. Among the most commonly used plastics are polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP). According to the "Plastics Market Analysis" report from Plastics News (2023), PE accounts for approximately 30% of the global plastic market due to its lightweight, flexibility, and high resistance to impact and moisture. This makes it an ideal choice for water storage and agricultural applications. On the other hand, PP is gaining traction, particularly in chemical storage. It offers superior chemical resistance and can withstand higher temperatures, with a melting point of approximately 170°C, as noted in the "Polymer Properties Database."
In addition to PE and PP, other plastics such as PVC and PVDF have their unique advantages. PVC is often favored for its strength and durability, making it suitable for wastewater treatment applications. Meanwhile, PVDF, known for its exceptional chemical and thermal resistance, is often used in the pharmaceutical and food industries. The 2023 "Global Plastic Materials Report" indicates that while PE remains the dominant player, specialty plastics like PVDF are projected to see a 15% increase in usage over the next five years, driven by rising demands in regulatory-sensitive environments. Understanding these materials’ properties can significantly impact the longevity and performance of plastic tanks in diverse applications.
Assessing Environmental Conditions: UV Resistance and Temperature Tolerance
When selecting the right plastic tanks for your needs, it is crucial to evaluate the environmental conditions they will be exposed to. Two significant factors to consider are UV resistance and temperature tolerance.
Plastic tanks used outdoors will be subjected to sunlight, which can lead to degradation over time if the material lacks proper UV protection. Choosing tanks with UV-stabilized materials can prevent cracking, fading, and weakening, ensuring their longevity and reliable performance in harsh sunlight.
In addition to UV resistance, temperature tolerance is critical for maintaining the integrity of the tank and its contents. Extreme temperatures can affect the plastic's structural integrity, potentially leading to warping or brittleness. It's essential to select tanks capable of withstanding the temperature fluctuations typical of your region, whether they are high heat or freezing conditions.
Understanding the specific requirements of your storage contents alongside environmental factors will help you make an informed decision, ensuring your plastic tanks effectively serve their purpose without compromising safety or quality.
Cost-Effectiveness: Analyzing Long-Term Value versus Initial Investment
When selecting the right plastic tanks, assessing cost-effectiveness is crucial. The initial investment can often be a deterrent, especially when faced with various options on the market. However, a thorough analysis of long-term value is imperative to making a sound decision. Consider the lifespan of the tank, its durability, and maintenance requirements. While a cheaper tank may seem appealing upfront, hidden costs such as frequent repairs or replacements can add up significantly over time, overshadowing the initial savings.
Moreover, the intended use of the tank should guide your assessment of its total cost of ownership. For instance, a tank designed for high-impact environments or extreme temperatures may be priced higher initially but can provide significant savings due to reduced failure rates and lower maintenance costs. Evaluating these factors helps ensure that you are not only making a financially sound choice but also selecting a tank that aligns with your operational needs and sustainability goals.